Vein Function & Structure the difference between an artery vs veins, and the structure of veins they must leak out of the system through the capillary bedsExplain the relationship between the structure and function of arteries, This is because blood does not flow in pulses and so the vein walls cannot help pump the blood are made up of a wall that is only one cell layer thick and results in the distance for diffusion in and out of the capillary being very small so that diffusion can occur Locate the layers/structures of the vein, artery, and capillary
Tunica Tunica Artery Vein Capillary Ppt Download
Artery vein capillary structure
Artery vein capillary structure-Capillaries connect the smallest branches of arteries and veins The walls of capillaries are just one cell thick Capillaries therefore allow the exchange of molecules between the blood and theIt needs to get oxygen and nutrients from the top to the bottom of your body and it manages this with the help of the body's circulatory system The body has a network of blood vessels that carry blood around The way it works is quite similar to how traffic runs on the roads




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels
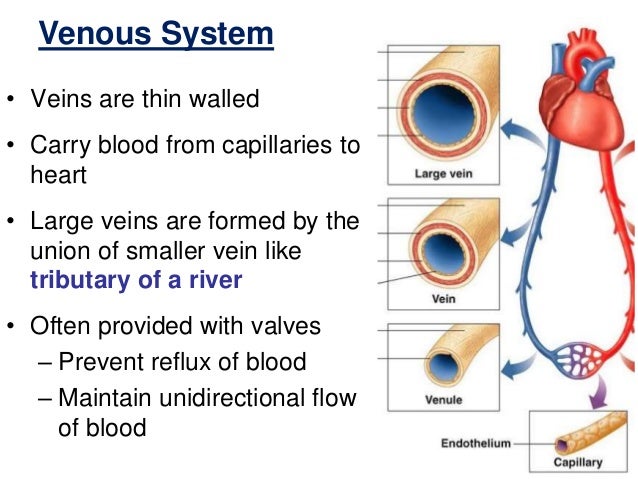
Capillaries are small but they have several important functions We'll go over the functions of different types of capillaries and what can happen when they don't work properly The capillaries fulfill the function of "bridge" The capillaries lie between the veins and the arteries That is, they are ramifications that leave the arteries and rejoin to form veins 4 Fig Structure of Blood Vessels Valves 1 Valves are present in veins except for pulmonary vein and not in arteries except pulmonary artery and aorta in which valve is there 2 It prevents the backflow of blood in veins, ie, ensures the flow of blood in one direction
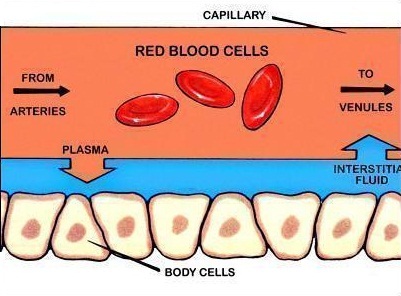
Procedure Microscopic Study of Arteries and Veins 1 The following slide are available for this study arteryveincapillaries, mammal 2 What Are the Structures and Functions of Capillaries and Veins?A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter, and having a wall one endothelial cell thick They are the smallest blood vessels in the body they convey blood between the arterioles and venules These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them
Eventually, the smallest arteries, vessels called arterioles, further branch into tiny capillaries, where nutrients and wastes are exchanged, and then combine with other vessels that exit capillaries to form venules, small blood vessels that carry blood to a vein, a larger blood vessel that returns blood to the heartStructure and Function of Blood Vessels small blood vessels that carry blood to a vein, An arteriole is a very small artery that leads to a capillary Arterioles have the same three tunics as the larger vessels, but the thickness of each is greatly diminished Structure Veins, much like arteries etc are exchanged between the blood and the surrounding tissues Structurally, a capillary is only one cell thick, so it's basically only one layer of endothelial tissue on a basement membrane Arteriosclerosis is associated with the thickening and loss of elasticity of the artery,



Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 14




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii
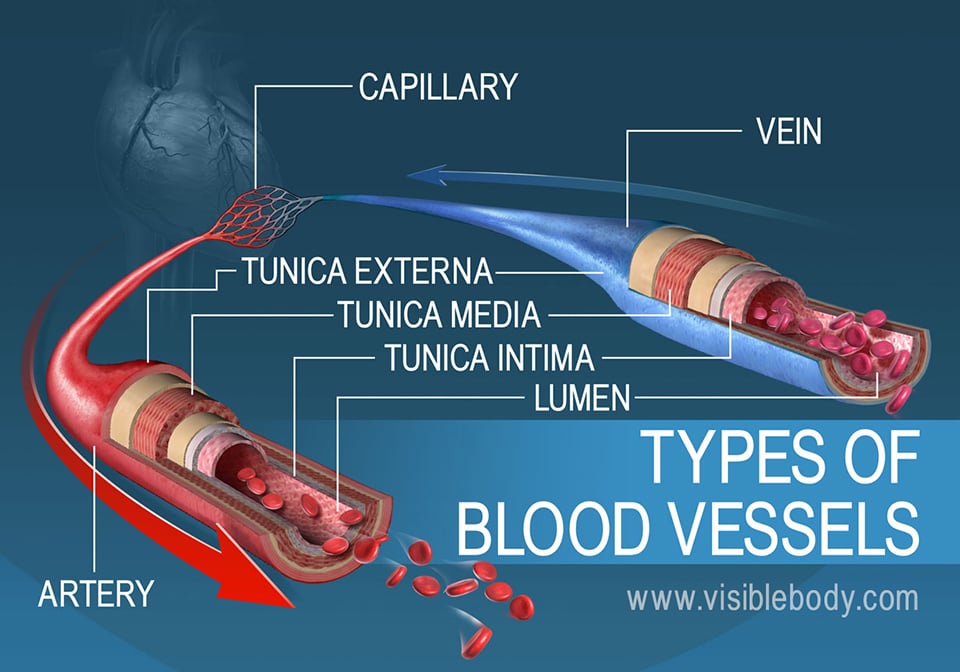
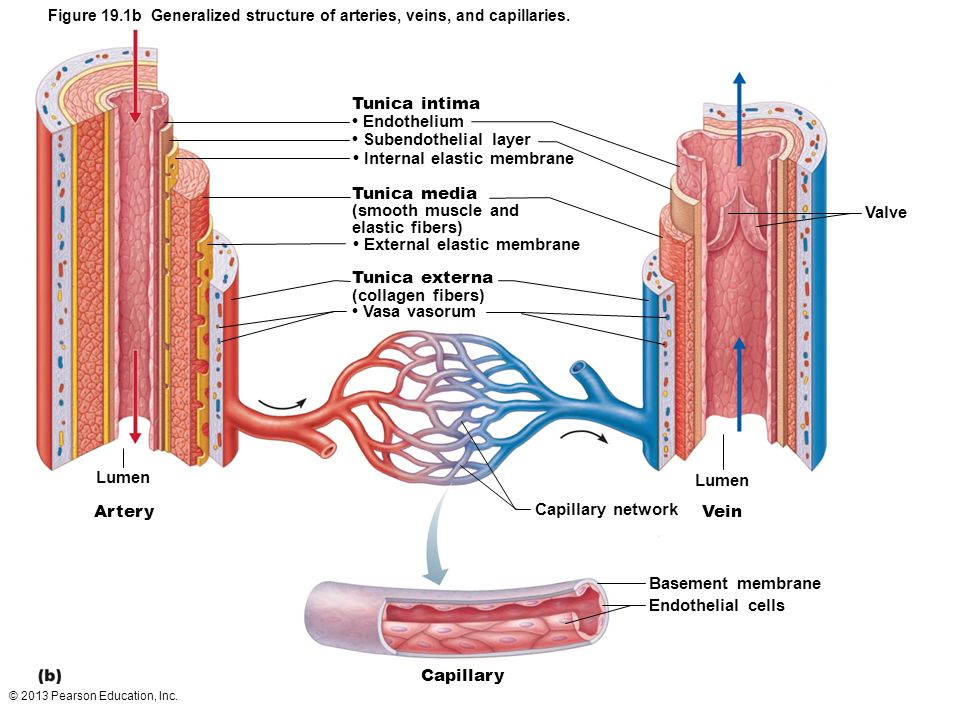
Circulatory System Artery, Vein and Capillary In this video I outline the structural and functional differences between the three blood vessels in the bodyComparative Structure of Artery and Vein Vessel Walls • Arteries 1 Tunica Interna aThe structure of the vessels is shown below Artery • It has a thick tunica externa which is an outer covering of tough collagen fibres • It has a tunica media which is a middle layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres • It has a lining of squamous endothelium (very thin cells) • It can contract using its thick muscular layer Capillary




Blood Vessel Structure And Function Artery Vein And Capillary Youtube



Blood Vessels Mind Map
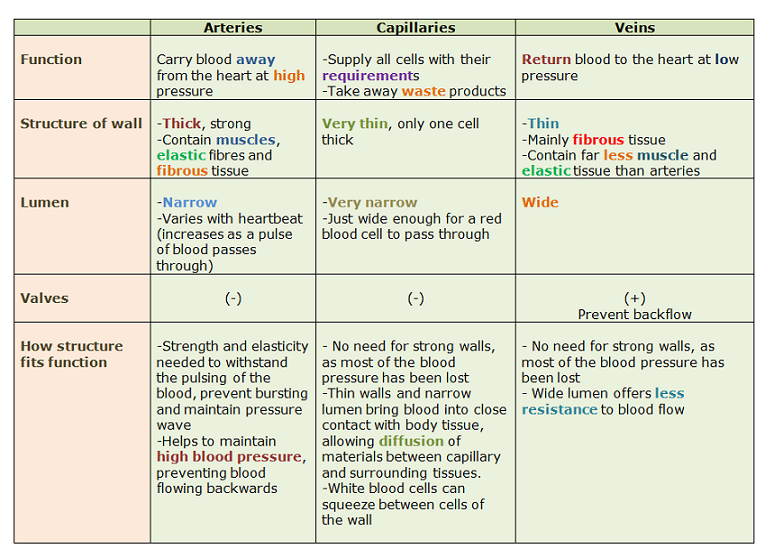
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels where the smallest arteries meet the smallest veins and where the blood exchanges food and oxygen for waste products Veins, which are also blood vessels, return depleted blood to the heart Some capillaries are so small that they can only be seen Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels Arteries take blood away from the heart The main artery is the aorta that branches into other major arteries, which take blood to different limbs and organsTable Comparing Arteries, Capillaries, and Veins Arteries Capillaries Veins blood moves away from the heart blood supply at tissue level blood returned to the heart thick middle layer of involuntary muscle to increase or decrease diameter one layer of




Blood Vessels Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock




Artery Vein Capillary High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
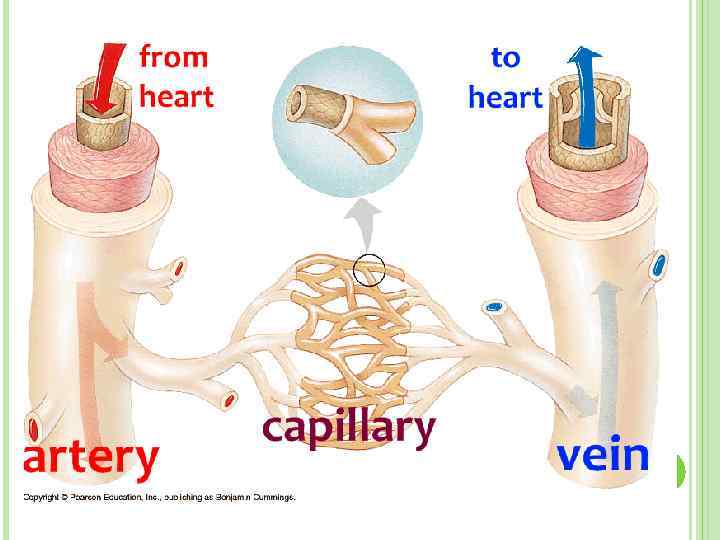
Arterioles diverge into capillary beds Capillary beds contain a large number (10 to 100) of capillaries that branch among the cells and tissues of the body Capillaries are narrowdiameter tubes that can fit red blood cells through in single file and are the sites for the exchange of nutrients, waste, and oxygen with tissues at the cellular level Fluid also crosses into theCapillaries, the smallest and most numerous of the blood vessels, form the connection between the vessels that carry blood away from the heart (arteries) and the vessels that return blood to the heart (veins) The primary function of capillaries is the exchange ofArtery vein capillary structure 19 Explain the relationship between the structure and function of arteries, and having a wall one endothelial cell thick, are the smallest of the body's blood vessels at between 510 What Are




Circulatory Systems



Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy
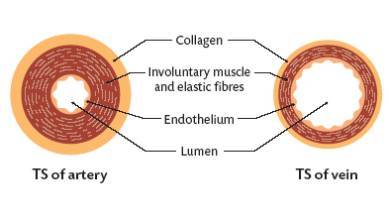
Vein blood is always deoxygenated apart from the pulmonary vein which carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart Both veins and arteries have An outer covering of tough collagenStart studying Artery, Veins, Capillary structure Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Artery, Vein, And Capillary Anatomical Structure In Detail Artery, Vein, And Capillary Anatomical Structure In Detail In this image, you will find endothelium, basement membrane, internal elastic lamina, smooth muscle, external lamina, tunica external, valve, lumen, the capillary in it Our LATEST youtube film is ready to run




Types Of Blood Vessels Structure And Function Of Arteries Arte Rioles Capillaries Venules And Veins Earth S Lab




40 3b Arteries Veins And Capillaries Biology Libretexts
I intend to explore the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries When an artery branches into smaller and smaller vessels, eventually the blood vessel is too small to see with the naked eye At that point, it is called an arteriole Likewise, a venule is a microscopic vein ArteriesThese grades are the stepping stone to your future Even if you don't want to stud Capillary Blood Samples Most of the time when you have your blood drawn, a technician will take blood from a vein in your arm Capillary blood may also be used to do some blood tests, such as for those who monitor their blood sugar A lancet is used to cut the finger (cut capillaries) and can be used for testing blood sugar and blood pH




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii
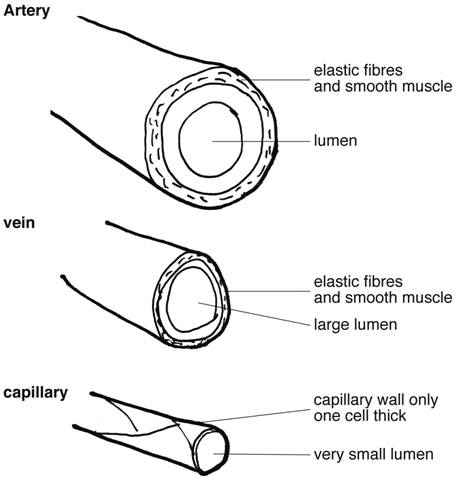



Blood Vessels
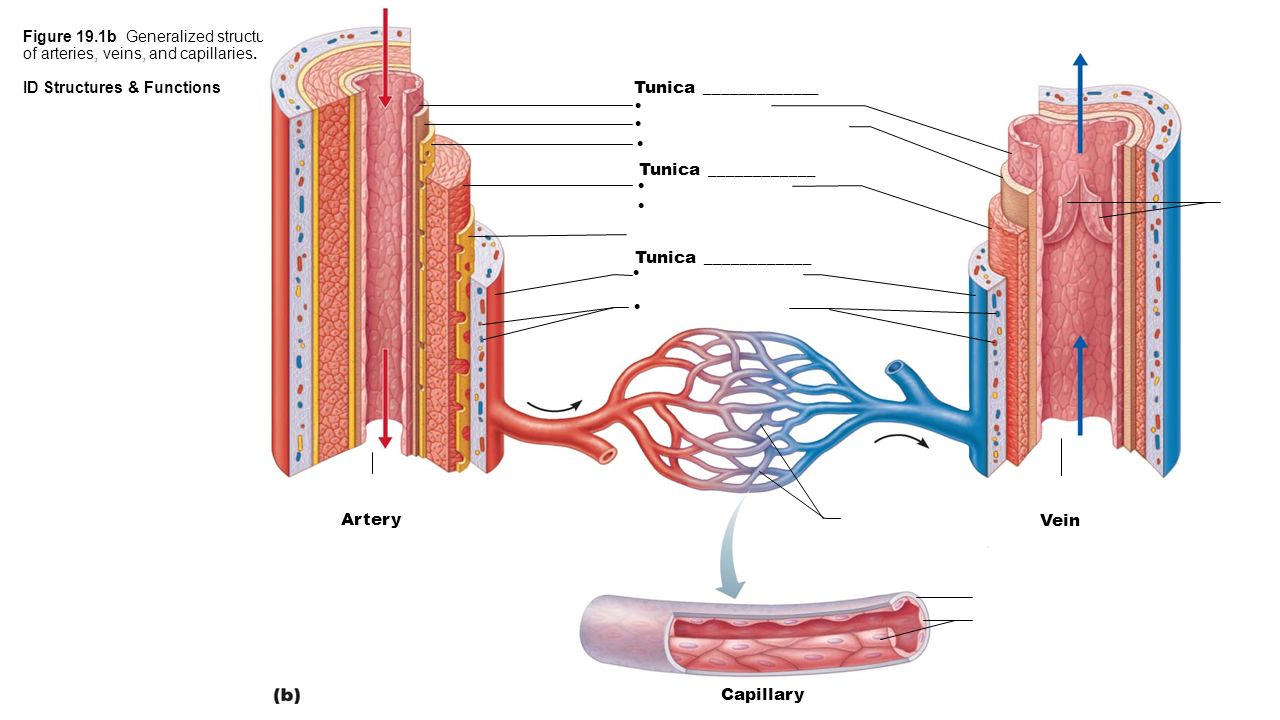
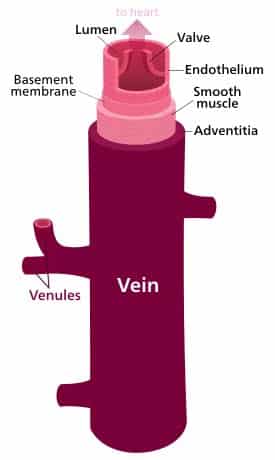
Vein – large veins, mediumsized veins, small veins and venules;© 14 Pearson Education, Inc Figure 181a Generalized structure of arteries, veins, and capillaries Artery VeinIn this laboratory you will study the microscopic/tissue structure of arteries and veins Focus Questions • What are the important differences in microscopic structure between an artery, vein and capillary?




Tunica Tunica Artery Vein Capillary Ppt Download
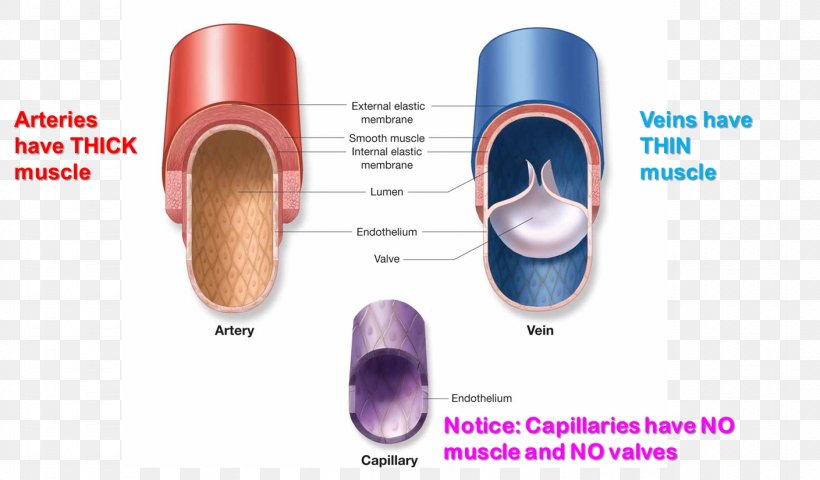



Capillary Pulmonary Artery Vein Function Png 1409x5px Capillary Anatomy Artery Blood Blood Vessel Download Free
A vein has the same three layers as the artery shown here, but the middle layer (tunica media) of a vein is thinner and lacks smooth muscle tissue The walls of both arteries and veins have three layers the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia You can see the three layers for an artery in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)The capillaries are the smallest segments of the circulatory system and are about as wide as the diameter of a red blood cell It is the area of the gas exchange between the blood and tissue spaces Structure of the Blood Vessels Since the diameter of a capillary is 510 μm, only a single file of blood vessels can pass through a capillary at a time The wall of the capillary is made up of simple squamous epithelium Therefore, the wall consists of a basement membrane and endothelial cells The structure of a capillary is shown in figure 1




Arteries Veins Capillaries




Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy
I want to help you achieve the grades you (and I) know you are capable of; 1Vein is a larger blood vessel compared to capillary 2Capillary can hold only 5% of the blood while the artery can hold up to 75% of blood at any time 3Veins contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood unlike the capillary 4Capillaries contain a single layer of wall while veins contain three layers of cell wallA capillary's diameter is so small that RBCs must pass through it in single file The walls of capillaries consist of an endothelium supported by a layer of areolar connective tissue These extremely thin walls facilitate the exchange of materials




Generalized Structure Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Diagram Quizlet



Humangallerypage2
There are 3 main kinds of blood vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries Arteries carry blood away from the heart They divide again and again, and eventually form very tiny vessels called capillaries The capillaries gradually join up with one another to form large vessels called veinsFunction Of Artery Vein And Capillary 1) these blood vessels are narrow and have very thin walls, they 1) these blood vessels have thick walls and carry blood from the heart to different body parts Source wwwpinterestcom 1) these blood vessels have thin walls and carry blood from different body parts to the heartVeins, Arteries and Capillaries Professor Hallux is here to explain!




Blood Collection Arteries Veins And Capillaries Circulatory System
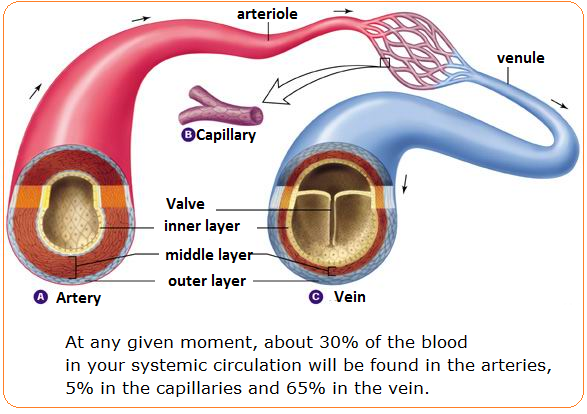



Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 14
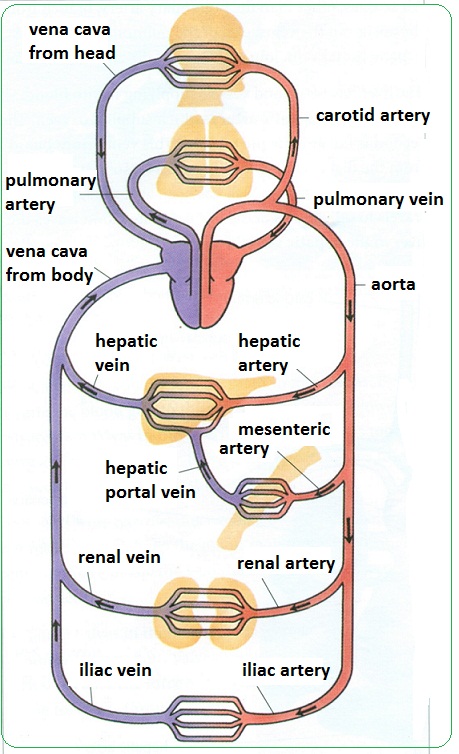
The structure and function of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries is vital for the circulatory system to work The overall function of the circulatory system is to transport blood and lymph around the body In doing so it delivers oxygen and nutrients to the body, removes waste products from the body, is involved in the HEART ARTERY ARTERIOLE CAPILLARY VENULEVEIN 4 • Carry blood away from the heart • "Branch" or "diverge" as they form smaller and smaller division • Thickwalls to withstand pressure produced when heart pushes blood into the arteries Elastic fibers (tunica media) allow the artery to stretch under pressureThe pulmonary vasculature is comprised of three anatomic compartments connected in series the arterial tree, an extensive capillary bed, and the venular tree Although in general this vasculature is thinwalled, structure is nonetheless complex
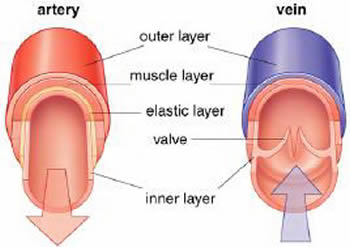



What Is The Relationship Between The Structure And Function Of Arteries Capillaries And Veins Socratic
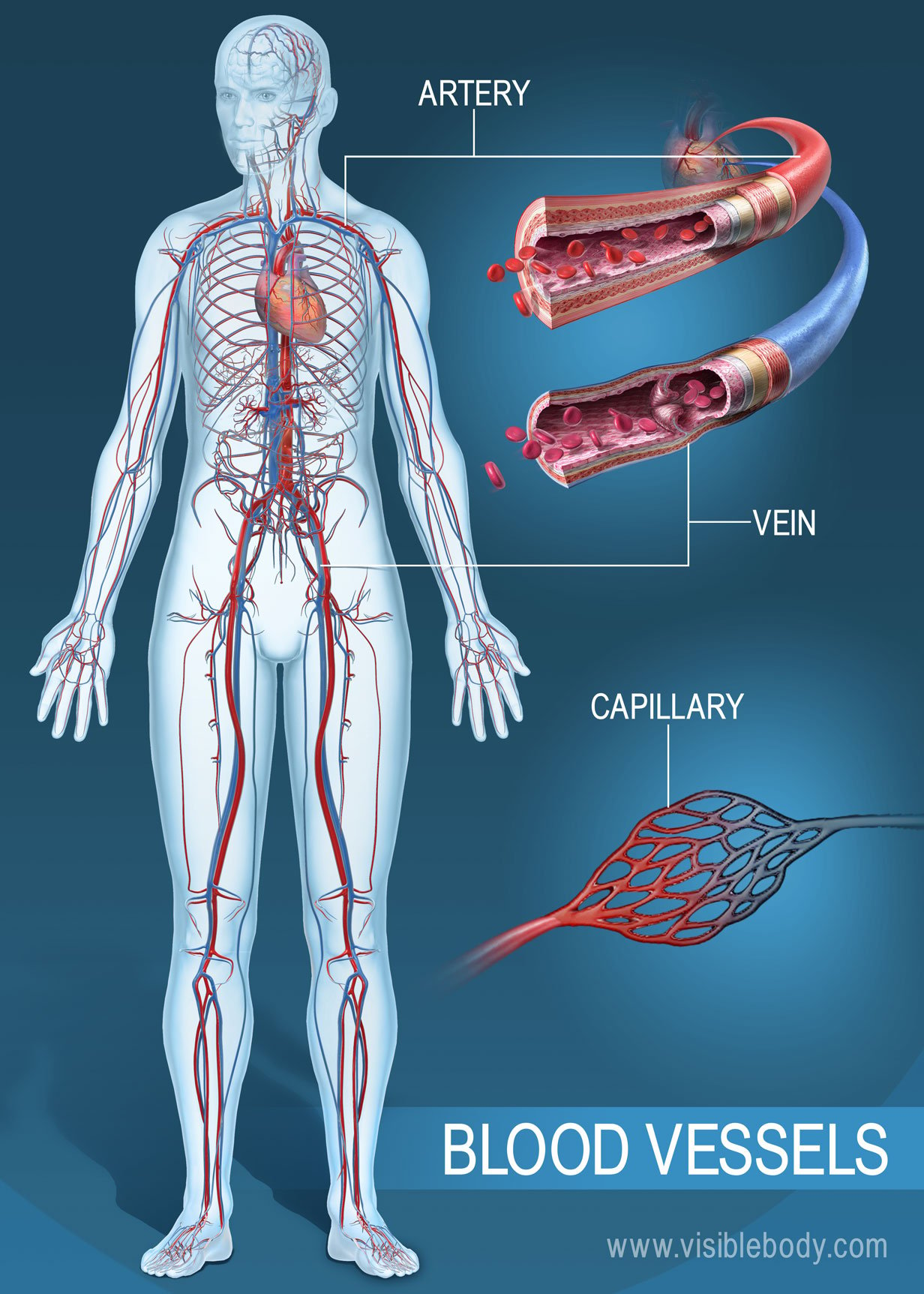



Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy
Capillaries make a capillary bed while veins are larger vessels The wall of the vein has three layers, while the wall of capillary has only one layer Most importantly, veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues and organs to the heart while capillaries facilitate the exchange of gas, nutrients, waste products, hormones, and many other constituents between the An artery's muscle helps it expand and contract in rhythm with the heart beating to keep blood moving through the system Capillaries connect veins and arteries to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide Thin and weak, capillaries are only as thick as one epithelial cell Blood passes through capillaries one cell at a time, single file JOHN BAVOSI/Science Photo Library/Getty Images An artery is an elastic blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart This is the opposite function of veins, which transport blood to the heart Arteries are components of the cardiovascular system This system circulates nutrients to and removes waste material from the cells of the body
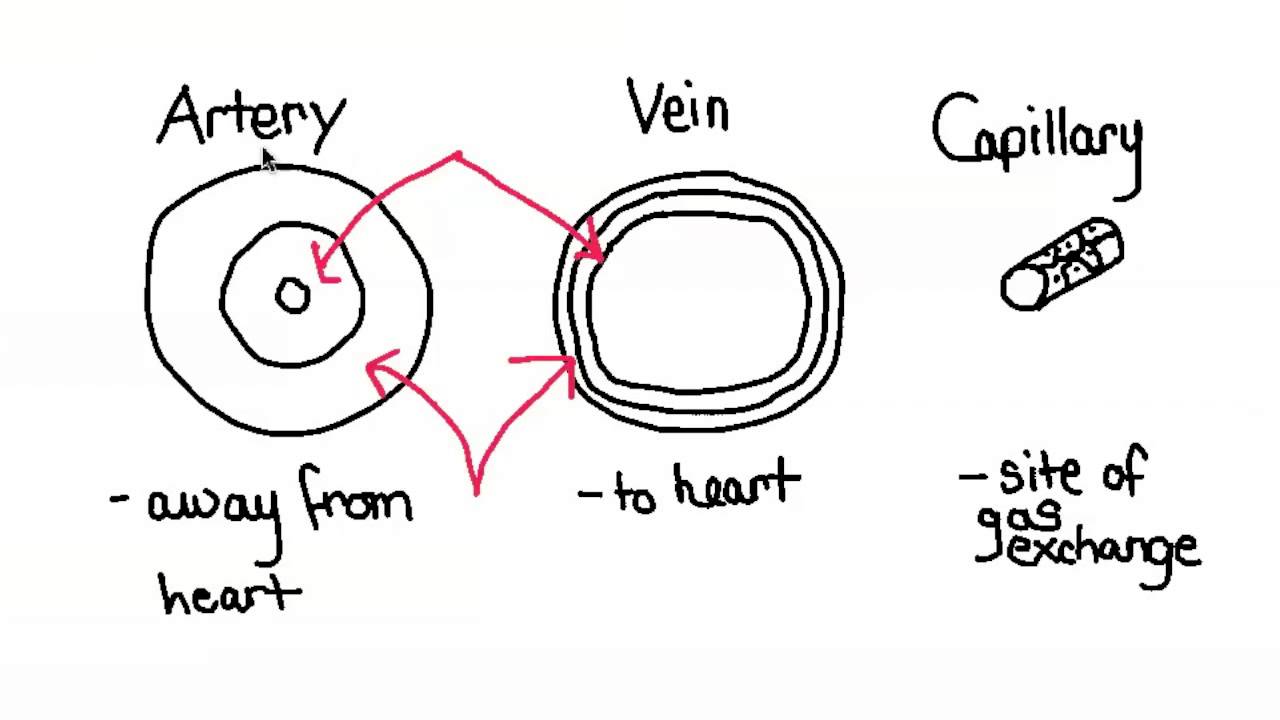



6 2 5 Relationship Between Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Youtube




Fox Run Equine Center Capillaries A Capillary Is An Extremely Small Blood Vessel Located Within The Tissues Of The Body That Transports Blood From Arteries To Veins Capillaries Are Most Abundant
Arteries move oxygenated blood away from the heart to other body organs while Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart On the other hand, capillaries transport blood away from the body and also allow the exchange of carbon dioxide, oxygen, nutrients and waste products in the body They also serve as a link between veins and arteries Artery Vein Capillary Structure Microcirculation deals with the circulation of blood from the heart to arteries, to smaller arterioles, to capillaries, to venules, to veins and back to the heart Instead of having a continuous layer of smooth muscle cells, intermediate rings of veins vary slightly in structure according to their sizeDescribe the basic structure of a capillary bed, small blood vessels that carry blood to a vein, An arteriole is a very small artery that leads to a capillary Arterioles have the same three tunics as the larger vessels, but the thickness of each is greatly diminished
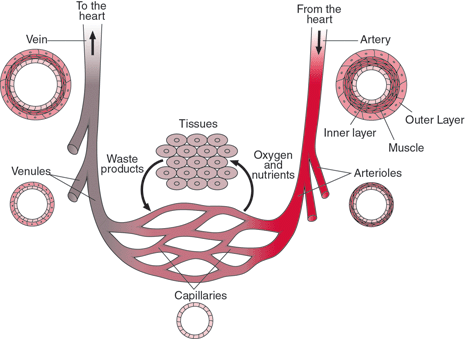



Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 14
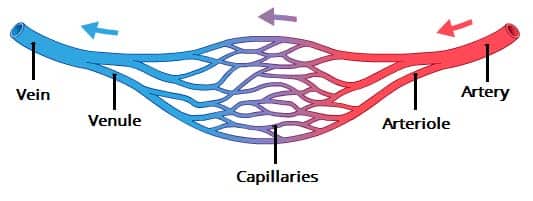



Ultrastructure Of Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Teachmeanatomy
Now remember the capillaries contain low pressure blood to pass on to veins so the veins don't need thick walls like arteries But without high pressure to keep the blood moving they will need a way to keep blood moving in the right direction (often against gravity ie from the leg) So that is the key differences between the structure of Venules are continuous with the postcapillary venules They continue to move blood away from the capillary beds Many venules unite to form a vein Structure The endothelium is associated with pericytes or thin smooth muscle cells (the beginning of a tunica media) to form a very thin wall Venules can have a diameter of up to 1mmStructure and function of arteries, capillaries and veins Blood is pumped from the heart in the arteries It is returned to the heart in the veins The capillaries connect the two types of blood




General Features Of Blood Vessel Structure




What Is The Difference Between An Artery And A Vein
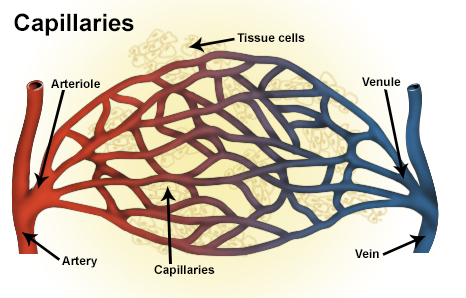



Seer Training Classification Structure Of Blood Vessels




Anatomy Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Ppt Video Online Download




Blood Vessels Cie Igcse Biology Revision Notes
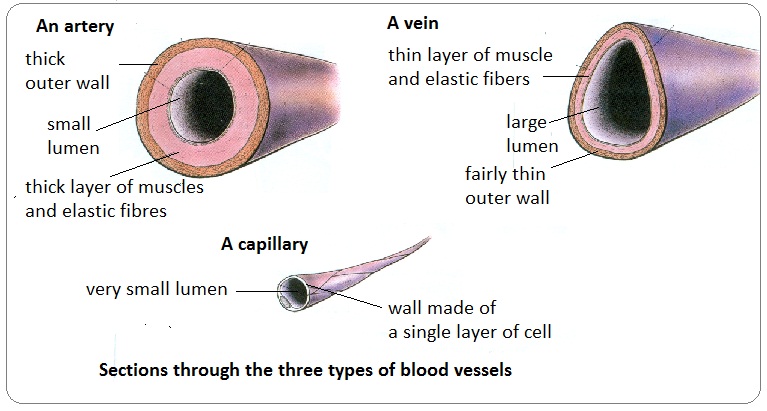



Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 14



Capillaries Structure Shefalitayal
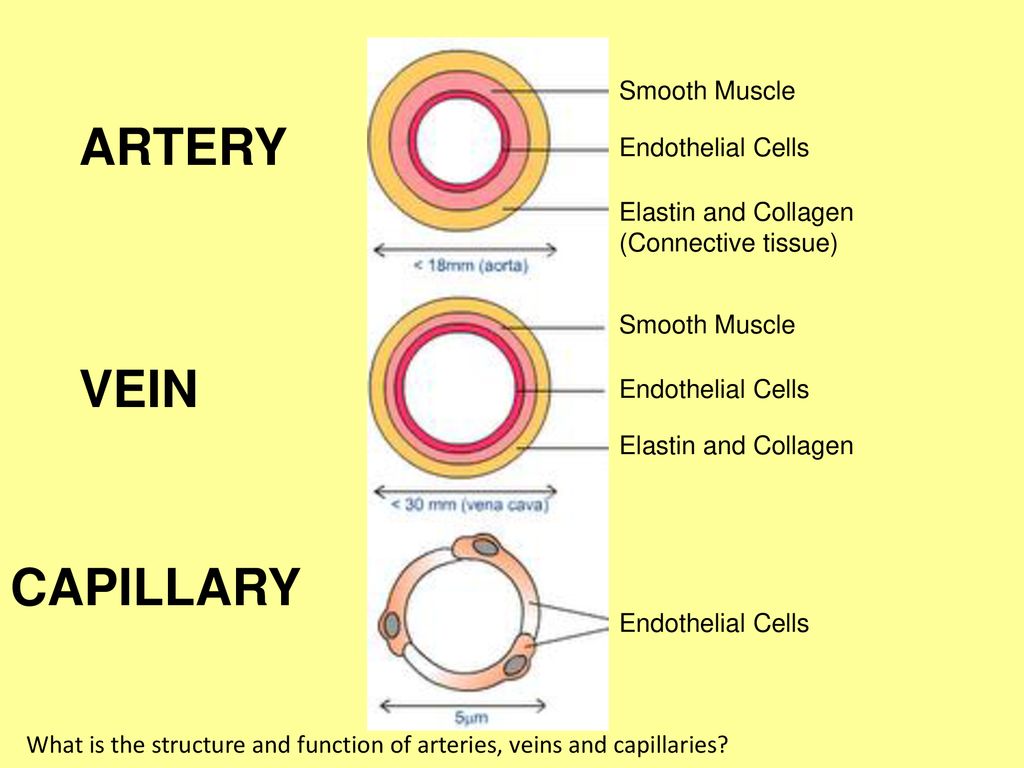



What Is The Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Ppt Download



Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries



1



Apii Notes Home Page



Components Of Blood Cardiovascular System Pass My Exams Easy Exam Revision Notes For Gsce Biology




Starter Compare The Structures Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries With Reference To Structure And Function Ppt Download




Vessel Comparison Bioninja




Arteries Veins Stock Illustrations 3 512 Arteries Veins Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Structure Of Blood Vessels Google Image Download Scientific Diagram




Cross Section Of Artery And Vein Interactive Anatomy Guide




Blood Vessel Definition Anatomy Function Types Britannica




Vasoconstriction The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




Lesson 5 Generalized Structure Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Diagram Quizlet



Arteries Veins And Capillaries Igcse Biology




27 Differences Between Arteries And Veins Arteries Vs Veins



Www Ocr Org Uk Images 2345 Unit J257 02 Depth In Biology Foundation Tier Paper 2 Sample Assessment Material Pdf




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels




Cardiac Blog 3 1 Relate The Structure Of The Arteries Veins And Capillaries To Their Functions




1 Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy Physiology




Question Video Comparing Structures Of The Three Main Types Of Blood Vessels Veins Arteries And Capillaries Nagwa




Chapter Blood Vessels Circulation




Topic Circulatory System Aim Describe The Structure And
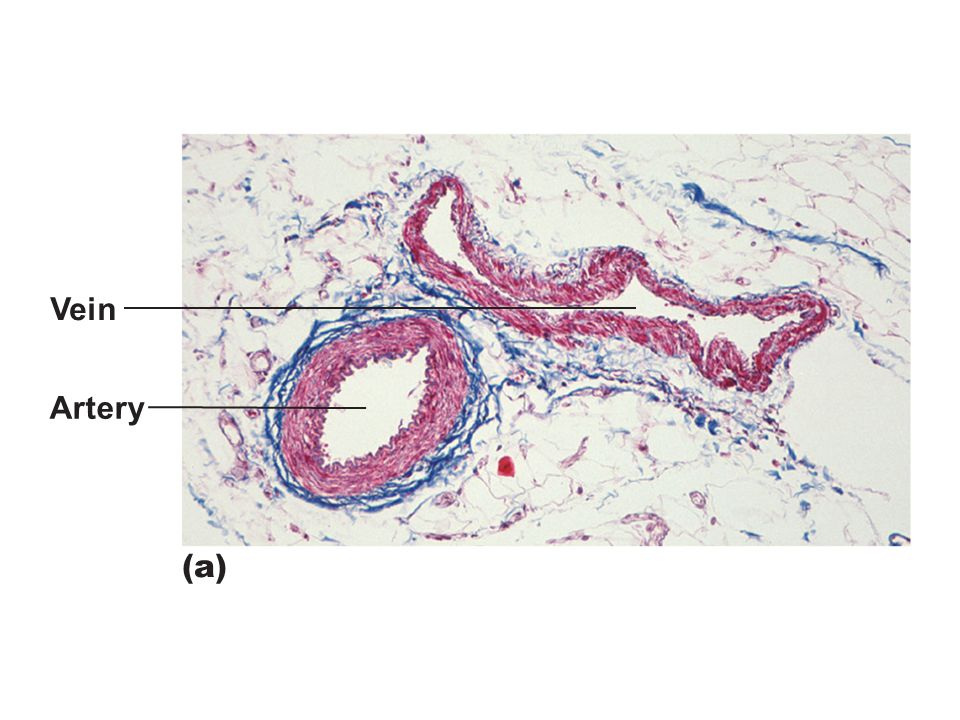



Figure 19 1a Generalized Structure Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Artery A Ppt Video Online Download
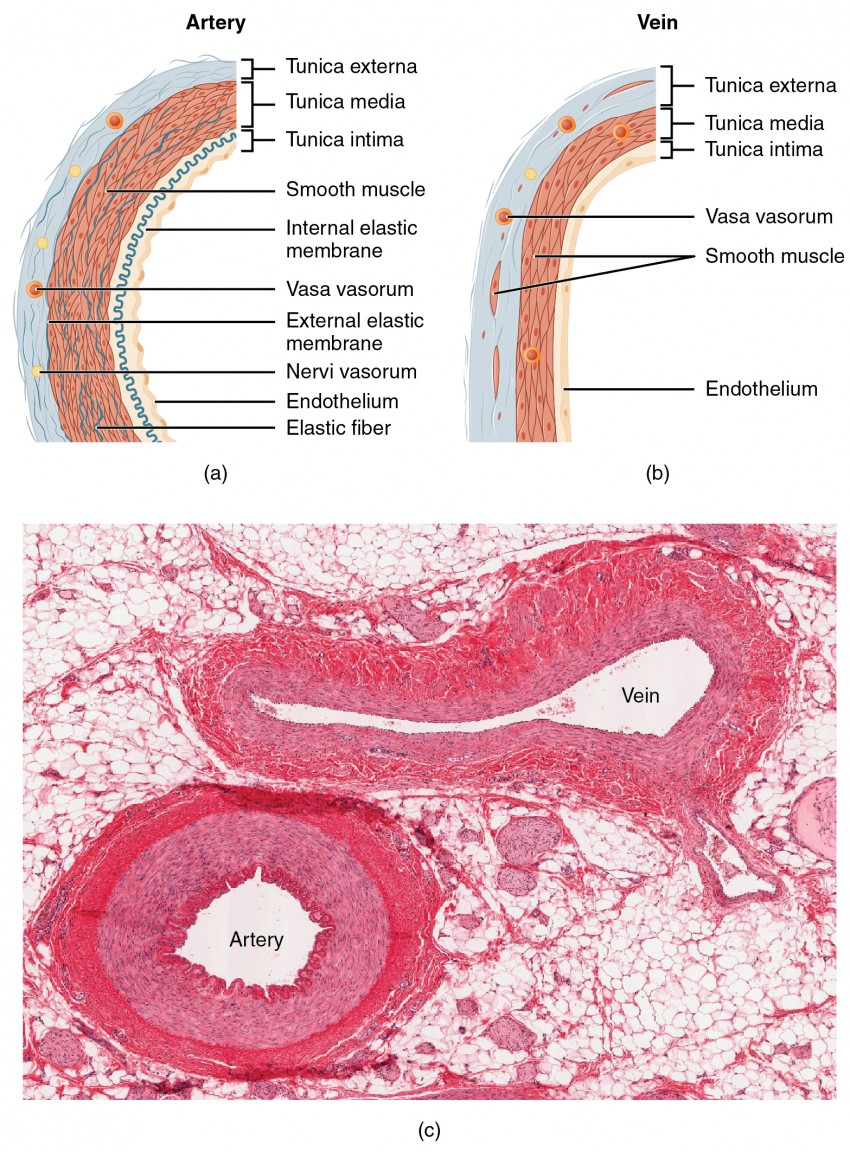



Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Blood Vessels Structures Functions Cie A Level Biology 19 21 Revision Notes




Arteries And Veins Stock Vector Illustration Of Biology




Blood Vessels Learning Objectives Compare And Understand The Difference In The Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins Capillaries Ppt Download
/GettyImages-464612781-edc0c4a8ab20491580bc3dd7acd4f4d2.jpg)



Capillary Structure And Function In The Body




Arterial And Venous Systems Arteries Arterioles Venules Veins Circulatory System Mcat Content




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii
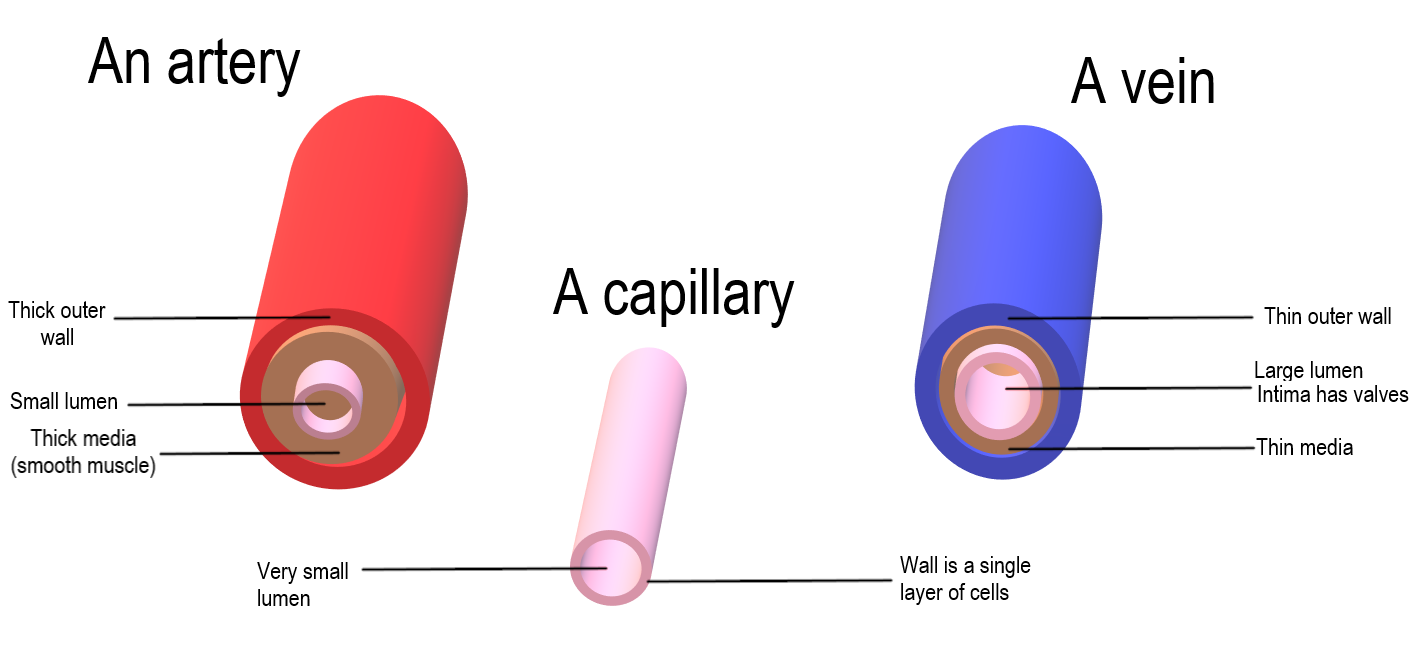



File Artery Vein Capillary Comparison Png Wikimedia Commons
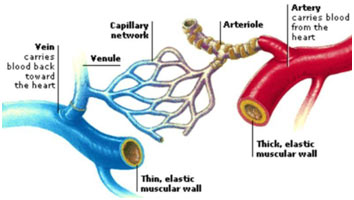



9 Difference Between Arteries Veins And Capillaries




Human Cardiac And Respiratory Systems Describe The Structure Of Arteries And Veins And Capillaries An In 21 Arteries And Veins Arteries Human Anatomy And Physiology




Arteries Veins And Capillaries Best Comparison Part 1 Youtube




Structure Of Blood Vessels
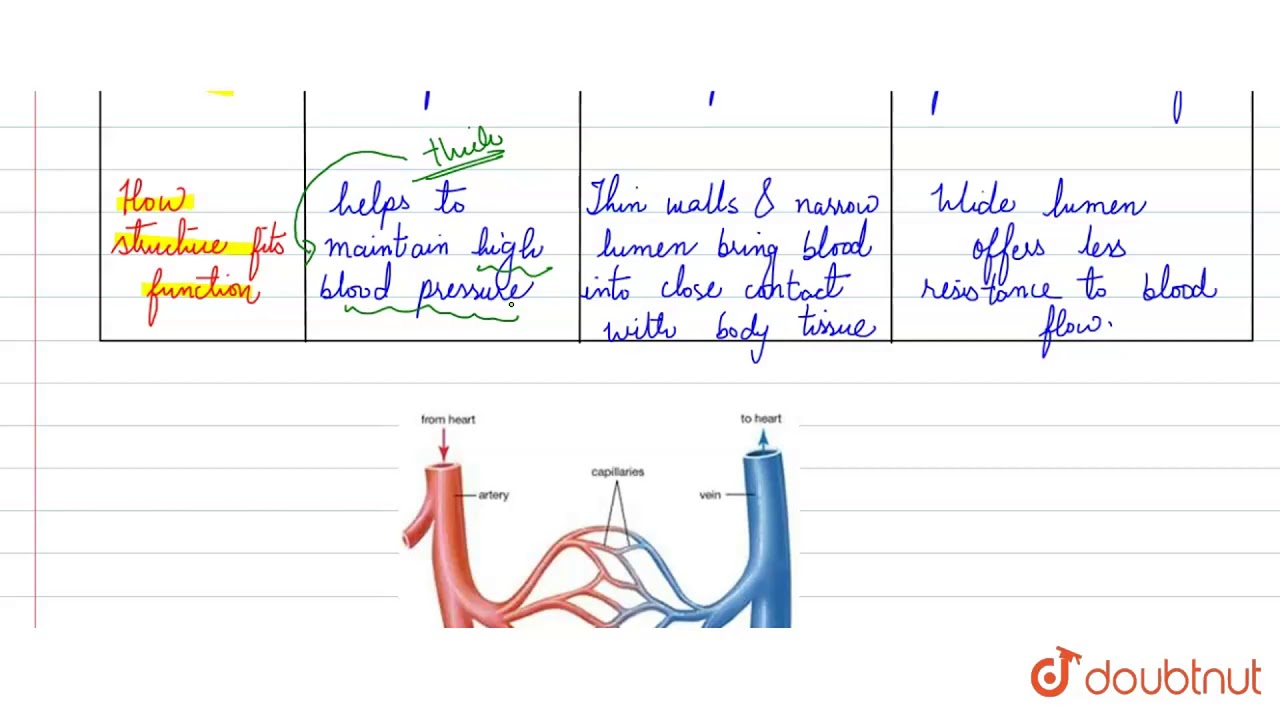



State The Differences Between Artery Vein And Capillary Youtube




Biology Gcse Revision 2 65 Describe The Structure Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries And Understand Their Rol



1




Biology World 44 The Circulatory System Blood Vessels



Ultrastructure Of Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Teachmeanatomy



Histology Of Blood Vessels




Blood Vessel Structure And Function Artery Vein And Capillary In Hindi Bhushan Science Youtube



Blood Circulation And Heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Science



Blood Vessels Part 1 Slides By Barbara Heard And W Rose Ppt Download




Blood Vessels Artery Vein Internal Structure Stock Vector Royalty Free




As Level G 1 Arteries Veins Capillaries Ms Cooper Youtube




Vessel Comparison Bioninja



Human Circulatory System Functions Of Human Circulatory




Blood Vessel Structure And Function Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
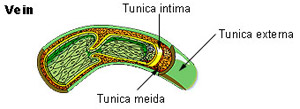



Seer Training Classification Structure Of Blood Vessels




Circulation And Gas Exchange Online Presentation




Lesson Explainer Blood Vessels Nagwa



Blood Vessel Anatomy



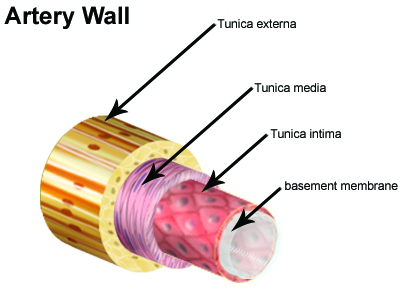
Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 14




Capillary Wikipedia



Seer Training Classification Structure Of Blood Vessels




1 Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy Physiology




Artery And Vein Human Circulation Artery And Vein Structure As A Human Circulation Concept With Blood Vessels Close Up In A Canstock




Arterioles Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Arteries Veins Capillaries Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



1



Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 14




40 3b Arteries Veins And Capillaries Biology Libretexts




Blood Vessels Knowledge Amboss



1




Ultrastructure Of Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Teachmeanatomy




Blood Vessel Structure Human Anatomy And Dissection Reader Openstax Cnx




Arteries Veins And Capillaries Access Revision




Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Biology 360




Hematology And Circulatory System Blood Heart Arteries Veins
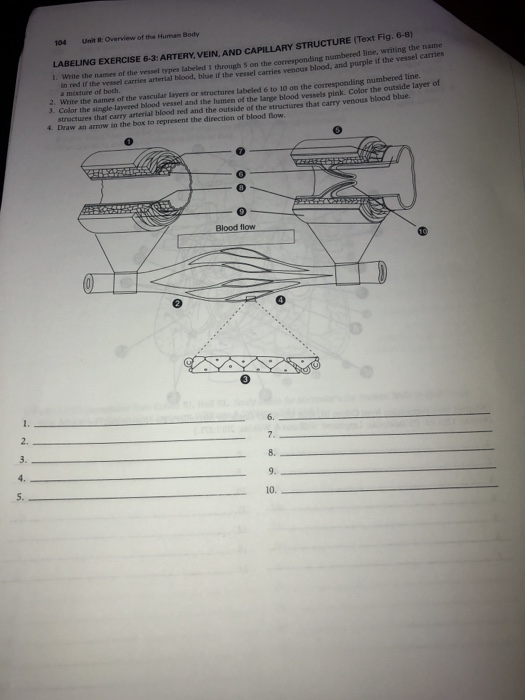



104 U Overview Of The Human Body The Labeling Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿